Calculating work needed to create an electric or magnetic field in unit volume (say, in a capacitor or an inductor) results in the electric and magnetic fields energy densities:
and
-
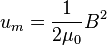 ,
,
in SI units.
Electromagnetic radiation, such as microwaves, visible light or gamma rays, represents a flow of electromagnetic energy. Applying the above expressions to magnetic and electric components of electromagnetic field both the volumetric density and the flow of energy in e/m field can be calculated. The resulting Poynting vector, which is expressed as
in SI units, gives the density of the flow of energy and its direction.
The energy of electromagnetic radiation is quantized (has discrete energy levels). The spacing between these levels is equal to
-
- E = hν
where h is the Planck constant, 6.6260693(11)×10−34 Js,[19] and ν is the frequency of the radiation. This quantity of electromagnetic energy is usually called a photon. The photons which make up visible light have energies of 270–520 yJ, equivalent to 160–310 kJ/mol, the strength of weaker chemical bonds.

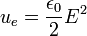



0 comments:
Post a Comment