An evolved, average-size star will now shed its outer layers as a planetary nebula. If what remains after the outer atmosphere has been shed is less than 1.4 solar masses, it shrinks to a relatively tiny object (about the size of Earth) that is not massive enough for further compression to take place, known as a white dwarf.[60] The electron-degenerate matter inside a white dwarf is no longer a plasma, even though stars are generally referred to as being spheres of plasma. White dwarfs will eventually fade into black dwarfs over a very long stretch of time.
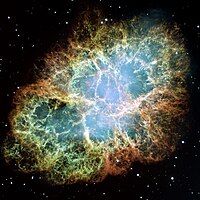
In larger stars, fusion continues until the iron core has grown so large (more than 1.4 solar masses) that it can no longer support its own mass. This core will suddenly collapse as its electrons are driven into its protons, forming neutrons and neutrinos in a burst of inverse beta decay, or electron capture. The shockwave formed by this sudden collapse causes the rest of the star to explode in a supernova. Supernovae are so bright that they may briefly outshine the star's entire home galaxy. When they occur within the Milky Way, supernovae have historically been observed by naked-eye observers as "new stars" where none existed before.[61]
Most of the matter in the star is blown away by the supernovae explosion (forming nebulae such as the Crab Nebula[61]) and what remains will be a neutron star (which sometimes manifests itself as a pulsar or X-ray burster) or, in the case of the largest stars (large enough to leave a stellar remnant greater than roughly 4 solar masses), a black hole.[62] In a neutron star the matter is in a state known as neutron-degenerate matter, with a more exotic form of degenerate matter, QCD matter, possibly present in the core. Within a black hole the matter is in a state that is not currently understood.
The blown-off outer layers of dying stars include heavy elements which may be recycled during new star formation. These heavy elements allow the formation of rocky planets. The outflow from supernovae and the stellar wind of large stars play an important part in shaping the interstellar medium.



0 comments:
Post a Comment