An elastic force acts to return a spring to its natural length. An ideal spring is taken to be massless, frictionless, unbreakable, and infinitely stretchable. Such springs exert forces that push when

contracted, or pull when extended, in proportion to the displacement of the spring from its equilibrium position.[56] This linear relationship was described by Robert Hooke in 1676, for whom Hooke's law is named. If Δx is the displacement, the force exerted by an ideal spring equals:

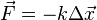


0 comments:
Post a Comment